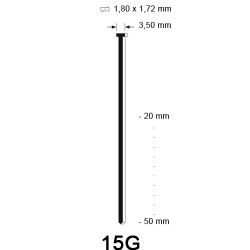
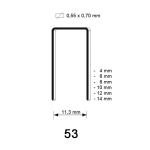
Wanneer je bezig bent met de afwerking van een project, dan kun je hierbij gebruikmaken van afwerknagels. Deze afwerknagels staan ook wel bekend als brads. Maar welk type afwerknagel is voor jouw afwerking geschikt? In deze blog gaan we je helpen met het maken van je keuze. Om je op weg te helpen, bespreken we de verschillende types afwerknagels en wat hun meest gebruikte toepassingen zijn. Lees verder om meer te leren!
Wat zijn afwerknagels?
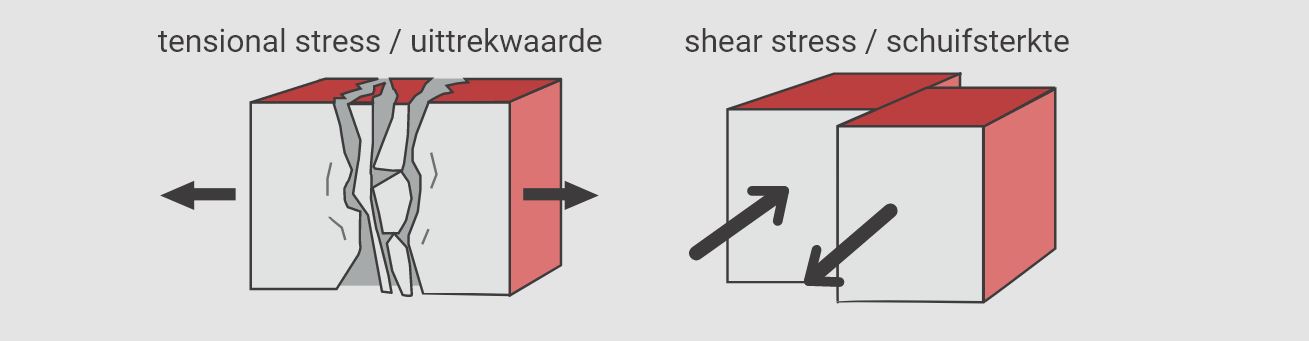
Afwerknagels of brads zijn kleine bevestigingsmaterialen die zorgen voor een nette en onopvallende afwerking. Brads zijn vooral geschikt voor het bevestigen van dunne en kwetsbare materialen. De afwerknagels zijn zo dun van formaat dat ze minder snel hout zullen splijten, maar het is wel belangrijk om te onthouden dat ze niet voor elk project geschikt zijn. Zo kun je ze niet gebruiken bij grovere constructie doeleinden. Gebruik hiervoor bevestigingsmateriaal met een grotere uittrekwaarde zoals spijkers of schroeven.
Verschillende soorten brads
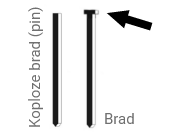
Qua vorm zijn er drie typen brads: standaard brads, pins en schuine brads. De standaard afwerknagels komen in rechte verlijmde strips en hebben een rechthoekige kop die de uittrekwaarde enigszins verbeteren. Ook bestaan er afwerknagels zonder kop. Deze staan bekend onder de Engelse benaming pins. De pins zijn nog minder zichtbaar dan brads, maar geven ook een minder stevige verbinding. Vaak worden ze gebruikt om materiaal vast te houden tijdens het lijmproces.
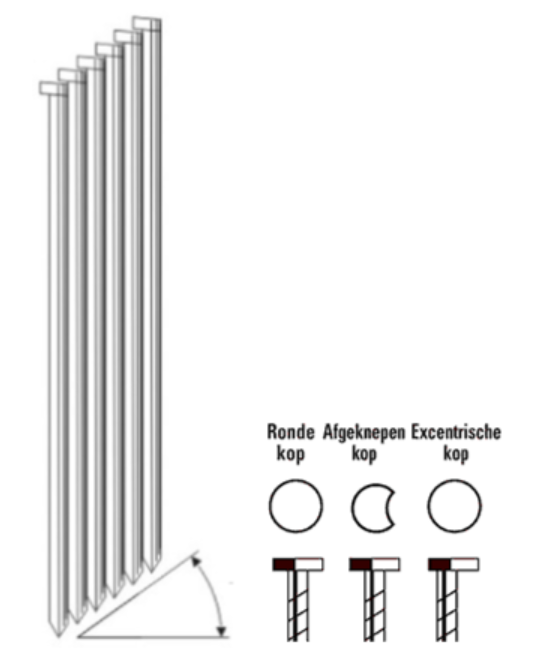
Als laatste bestaan er ook nog schuine brads. Dit betekent niet dat het bevestigingsmateriaal zelf schuin is, maar dat de strip met afwerknagels schuin met elkaar verbonden is. De strips komen in 25° en in 34°. Om dit mogelijk te maken, zijn de koppen van deze brads iets anders gevormd. Ze hebben namelijk een afgeknepen kop. Een voordeel van schuine brads is dat de apparaten waarin deze brads gaan compacter zijn en het makkelijker is om met deze bradtacker bij moeilijk bereikbare plekken te komen, zoals hoeken.
Verschillende maten brads
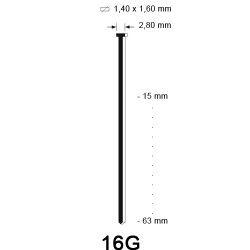
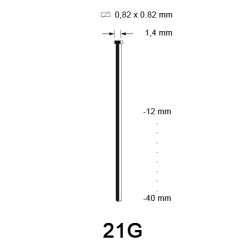
Naast soorten komen afwerknagels ook voor in verschillende maten. Welke afwerknagel het best geschikt is voor jou, hangt af van de toepassing waarvoor je deze gaat gebruiken. Bekijk het onderstaande overzicht, waar je de beschikbare maten brads en pins kunt inzien. Verder is het ook goed om te weten dat schuine brads in twee verschillende dikte maten: 15G en DA (1,8 mm) komen. Ook hebben de DA brads een ander puntafwerking, zodat er netter in materiaal geschoten kan worden.
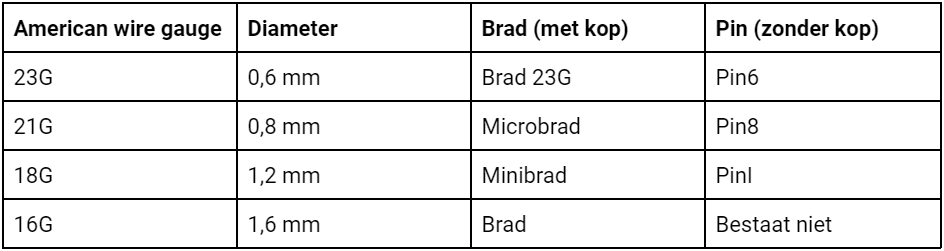
Om je een voorbeeld te geven van de diverse toepassingen van deze brads en pins, hebben we iedere American wire gauge apart genomen:
- 15G en 16G brads: voor het vastzetten van schrootjes en deurposten
- 18G (minibrad): om plinten mee vast te schieten
- 21G (microbrad): voor het vastschieten van parketvloeren
- Brad 23G: voornamelijk voor toepassingen waarbij de bevestiging vrijwel onzichtbaar moet zijn. Een toepassing voor deze brad is bijvoorbeeld voor het bevestigen van visgraat parket
Hieronder hebben we een overzicht van de verschillende diktes brads in hout geschoten:

Wat zijn de materiaaltypes voor afwerknagels?
Naast de vorm en de dikte van de afwerknagel is het ook belangrijk om de materiaalkeuze van de afwerknagels te overwegen. Er zijn over het algemeen vier materiaaltypes voor afwerknagels, met elk zijn eigen eigenschappen: gegalvaniseerd, roestvrij staal (RVS), extra gehard en polymeer. We gaan elk materiaaltype langs om je meer te vertellen over de eigenschappen en geschikte toepassingen.
Gegalvaniseerde brads
De meest voorkomende materiaalkeuze voor afwerknagels is gegalvaniseerd. Bij het galvaniseren van staal wordt de oppervlakte van staal voorzien van een laag zink met behulp van elektriciteit. Hierdoor is het mogelijk een zeer dunne laag zink op het materiaal aan te brengen. Ook is het goed bestand tegen krassen en vormt het zink bij beschadigingen een extra beschermlaag die verder roesten voorkomt. Gegalvaniseerde afwerknagels worden voornamelijk gebruikt voor afwerkingen voor in het interieur.
RVS brads
Roestvrij stalen brads zijn goed beschermt tegen roest. Bij blootstelling aan bepaalde weersomstandigheden of bijvoorbeeld zout water raden wij aan om te kiezen voor RVS afwerknagels te kiezen. Een nadeel van RVS is echter dat het aanzienlijk duurder is dan gegalvaniseerd staal, vanwege het hoge nikkelgehalte. Nikkel is een kostbaar materiaal dat aanzienlijk bijdraagt aan de prijs van RVS bevestigingsmateriaal.
Extra geharde brads
Voor het bevestigen in extra harde materialen kan er gekozen worden voor extra geharde afwerknagels. Deze High Carbon afwerknagels komen ook met een speciale punt om door te dringen bij hard materiaal. Met deze extra geharde afwerknagels kan je bijvoorbeeld hout bevestigen aan steen, beton, metaal, harde houtsoorten en meer.
Polymeer brads
Wij beschikken over ons eigen assortiment afwerknagels gemaakt van polymeer. Polymeer composiet is het type plastic dat gebruikt wordt voor dit bevestigingsmateriaal. Deze polymer fasteners zijn 100% metaalvrij en worden gemaakt van een hoogwaardige kwaliteit plastic. De polymeer afwerknagels worden hierdoor ook vaak gebruikt om CNC-materiaal vast te zetten, aangezien het bitje van de CNC niet beschadigd wordt door het bevestigingsmateriaal.
Het polymeer bevestigingsmateriaal wordt voornamelijk gekozen vanwege twee hoofdredenen:
- Polymeer brads kunnen worden gesneden, gevormd en geschuurd worden, zonder dat het zaagbladen, schaven, boorbitjes of schuurbanden beschadigt
- Plastic bevestigingsmateriaal kan nooit roesten, vlekken of strepen achter laten op het materiaal
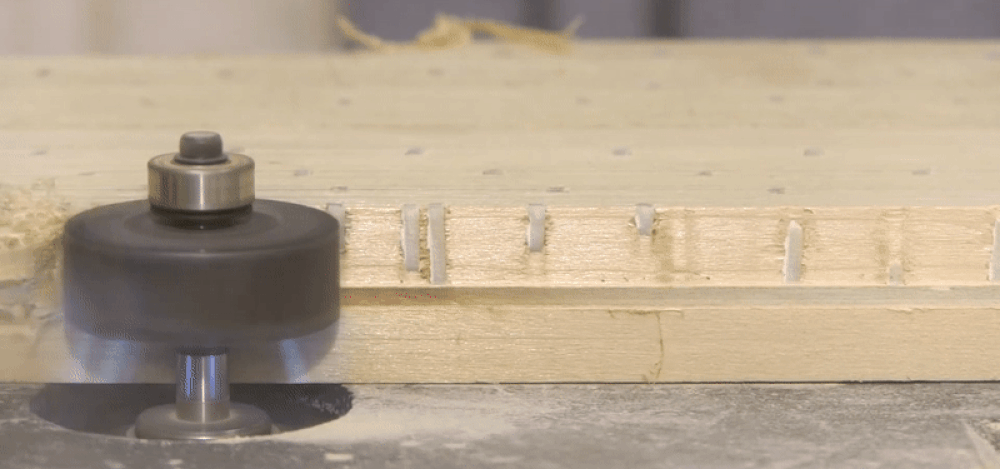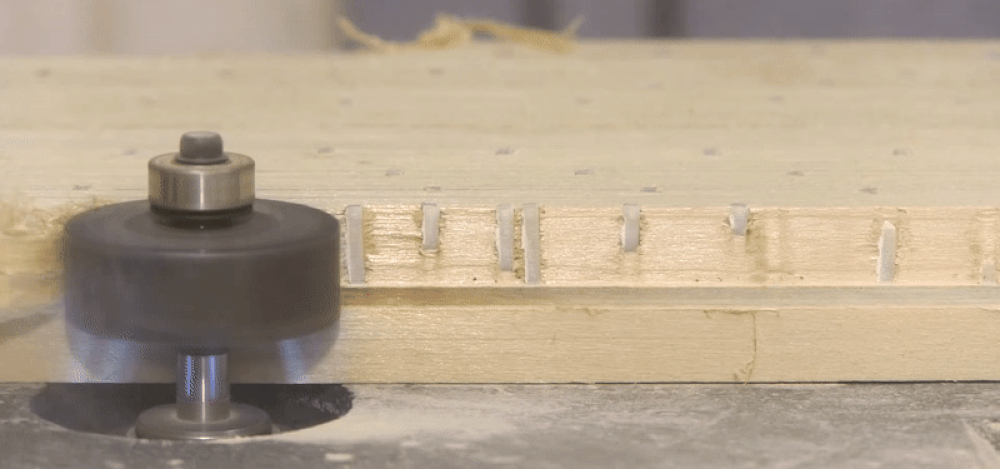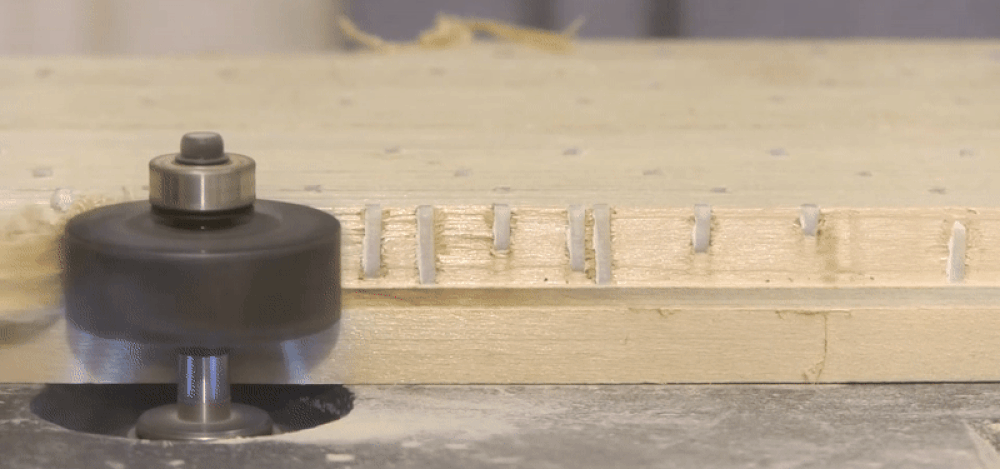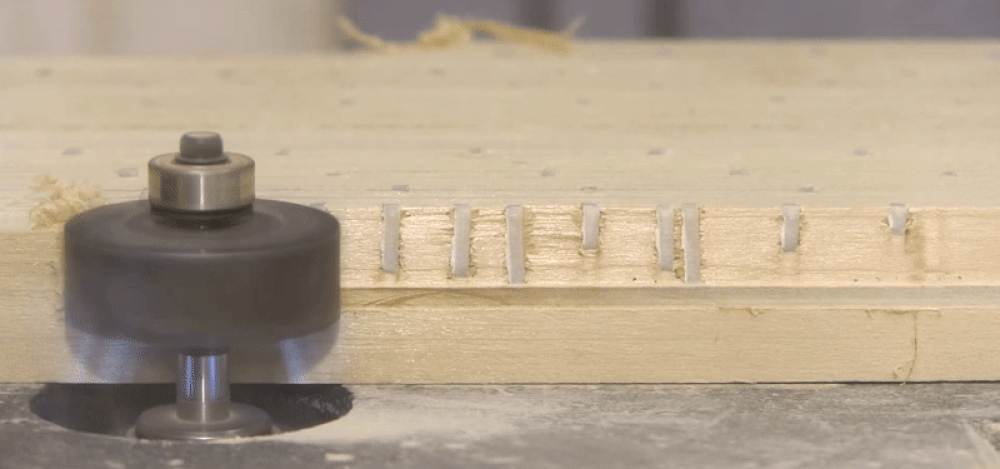
Ook hebben de afwerknagels van polymeer een hogere uittrekwaarde, aangezien het materiaal zich bij bevestiging verlijmd met de houtnerf. Echter is de schuifsterkte van de polymeer afwerknagel minder sterk dan staal. Ook heb je voor het schieten van polymeer afwerknagels specifiek gereedschap nodig, omdat polymeer bevestigingsmateriaal meer zijdelingse steun nodig heeft. De apparaten geschikt voor polymeer bevestigingsmateriaal hebben daarom een extra strak aandrijfmagazijn.
Wil je meer advies over afwerknagels?
Zoals je kunt lezen, zijn er veel verschillende soorten afwerknagels geschikt voor uiteenlopende toepassingen. Wil je graag zeker weten welke afwerknagels geschikt zijn voor jouw toepassing? Neem dan contact met ons op. Wij bieden altijd het beste advies en antwoorden op al je vragen. Neem contact op via ons contactformulier, stuur een e-mail naar info@bestfix.nl of bel ons direct op +31 (0)570 768 737.
-737x262.png)